Alternatives to leather: what developments?
Image courtesy of VitroLabs
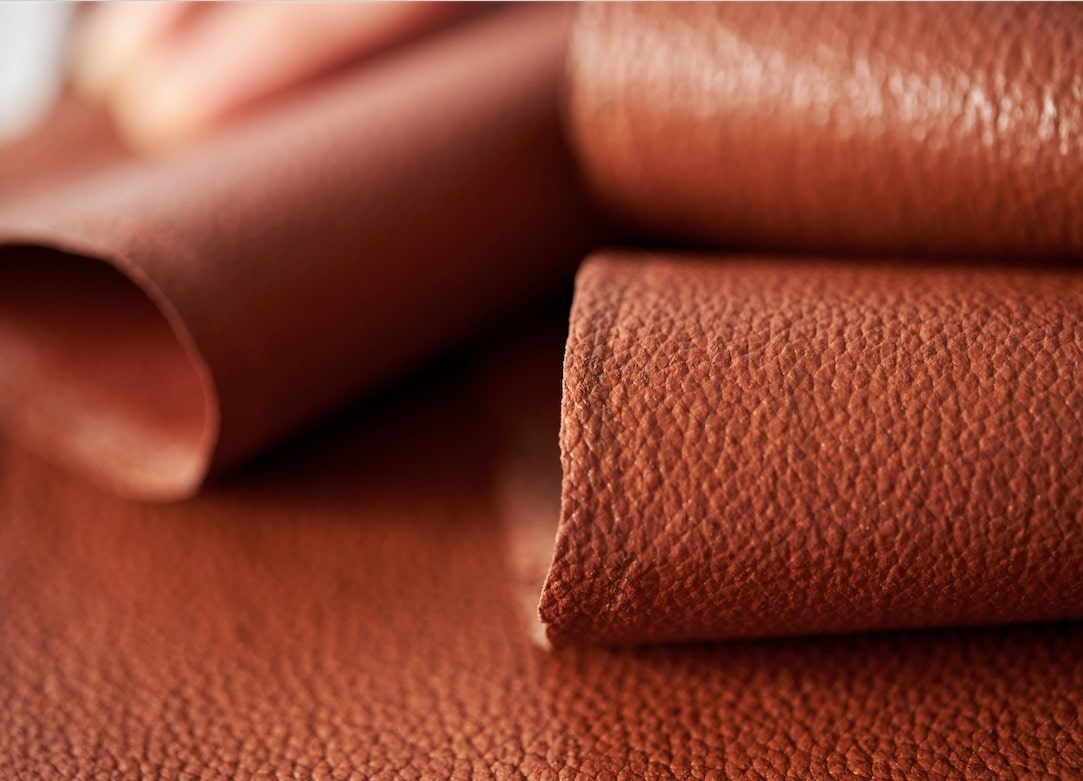
Leathers are natural and long-lasting materials long used in the fashion, furniture and automotive sectors.
In recent years, however, a discussion has opened around their use, triggered both by ethical, as they derive from animal slaughter, and environmental reasons. According to a UNIDO report on the carbon footprint of leather, in fact, the production of 1sqm of bovine leather generates approximately 110 kg of CO2eq.
The result of this awareness is the growing interest in the development of alternative solutions to leather of animal origin, which has seen a decisive boost in recent years also thanks to increasingly important investments.
There are different types of alternative materials to leather with content from renewable or renewed sources, which we can briefly summarize as follows:
- microfiber materials with partially or totally recycled and/or biological origin content;
- fabrics coated with recycled and/or biological origin content; these are mostly conventional materials, in which particular attention has been paid to the raw materials, replacing the component of fossil origin and reducing the use of chemicals of concern;
- sheets with recycled and/or bio-based content, often with proprietary formulations;
- natural coatings resulting from cuts of various plants, wood, mushrooms, cork, banana leaves, etc.;
- hybrid materials, with high fiber content and the presence of a certain quantity of binder;
- materials obtained through bio-manufacturing processes.
There are three trends in particular that we observe.
The first consists in the use of waste, typically deriving from the agri-food industry, as raw materials. Among the examples we can include leather based on the processing of industrial by-products of oranges and cactus blades, which avoid the environmental and economic costs associated with their disposal; leather made from grape waste from winemaking, vegetable oils and natural fibers of agricultural origin; or even leather that ingeniously exploits waste from tea processing, which would otherwise be disposed of in landfill or burned.

The second consists in the creation of completely bio-based mixtures, with natural rubber or bio-polymers used as binders.
Finally, the third is based on the exploitation of bio-manufacturing processes including bacterial cellulose, mycelium or cultivated proteins, which allow us to reduce carbon emissions.